Case report
Open Access
Open Peer Review
Published: 18 December 2019
Continuous intravenous low-dose diclofenac sodium to control a central fever after ischemic stroke in the intensive care unit: a case report and review of the literature
L. G. Giaccari,
M. C. Pace,
M. B. Passavanti,
P. Sansone,
V. Esposito,
C. Aurilio &
V. Pota
Journal of Medical Case Reports volume 13, Article number: 373 (2019) Cite this article
49 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Metricsdetails
Abstract
Introduction
Elevation in body temperature within the first 24 hours of ischemic stroke is fairly common and known to be associated with worse outcomes. Only after thoroughly ruling out infection and the noninfectious etiologies and in the appropriate clinical setting should the diagnosis of central fever be made. Acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are typical therapeutic options. External cooling is frequently used when pharmacologic interventions are inadequate. However, reports have suggested that neurogenic fevers are somewhat resistant to traditional pharmacologic therapies.
Case presentation
We describe a case of a Caucasian patient with central fever after ischemic stroke not responsive to acetaminophen administration and external cooling. After an initial bolus of diclofenac sodium (0.2 mg/kg in 100 ml of saline solution for 30 minutes), a continuous infusion (75 mg in 50 ml of saline solution) was started. After 5 days of treatment, the patient’s body temperature was below 37.5 °C, and the diclofenac sodium infusion was stopped.
Conclusions
We observed that a low-dose diclofenac sodium infusion was effective in treating fever without systemic side effects. This treatment may be suggested as an alternative to conventional antipyretic drugs, but additional clinical trials are required.
Open Peer Review reports
Introduction
Fever, defined as a core body temperature exceeding 37.5 °C, is common in patients with brain injury. It most often occurs within the first 2 days after a stroke, and its cause is not always easy to identify. In most cases, infection is the cause of fever after stroke. In severe stroke, massive tissue necrosis and the presence of blood in the brain can elevate body temperature [1].
Fever resulting from a stroke-related pathologic process starts within 24 hours of stroke symptoms, whereas fever of other etiologies emerges at later time points. If infections, venous thromboembolism, drugs reported to cause hyperthermia, and postsurgical origins are excluded, early fever in patients with stroke can indicate a neurological origin [1,2,3].
Elevation of temperature following stroke is likely the result of metabolic dissociation and heat production related to inflammatory cytokine release in response to the injury [3].
The relationship between fever, neurologic outcome, and stroke size is greatest when the increase in temperature begins within the first 24 hours of neuronal injury [3]. Fever is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in patients with stroke, independent of the temperature elevation origin [1,2,3].
International guidelines for patients with ischemic stroke recommend treating body temperature higher than 37.5 °C, searching for possible infection, and starting tailored antibiotic treatment. Multimodal cooling and antipyretics, such as acetaminophen, are recommended. The target temperature for patients with neurogenic fever is 37.0 ± 0.5 °C [1].
Case presentation
A 70-year-old Caucasian woman arrived at the emergency department of a local hospital few hours after a sudden loss of consciousness. Her medical history included type 2 diabetes mellitus being treated with oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin, untreated chronic atrial fibrillation, and transient ischemic attack about 10 years earlier.
On the basis of suspicion of stroke, computed tomographic angiography was performed, which revealed evidence of right middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion. Being within 6 hours of stroke onset, intra-arterial thrombectomy was performed, which did not resolve the occlusion. After 7 days of apparent clinical improvement, the patient had a rapid deterioration of the state of consciousness with acute respiratory failure, for which she was intubated, mechanically ventilated, and transferred to our intensive care unit (ICU).
At the time of admission, the patient presented with a state of neurological deterioration (Glasgow Coma Scale [GCS] score, 3) and a body temperature of 39 °C. Blood and urine tests, infection investigations, and chest x-ray were performed. Blood tests showed the absence of leukocytosis and negative C-reactive protein (CRP), whereas procalcitonin was not available at the time of admission to the ICU. Tests for urinary, pulmonary, and bloodstream infections required 48 hours for results. No abnormalities were observed on the chest x-ray. Tailored antibiotic treatment was initiated on the basis of suspicion of late-onset hospital-acquired pneumonia with piperacillin/tazobactam 4.5 g intravenously every 6 hours and linezolid 600 mg intravenously every 12 hours. The patient’s fever was treated with acetaminophen 1000 mg up to four times per day, which produced a nonsignificant reduction in body temperature. Brain computed tomography (CT) was performed, which confirmed the presence of an ischemic lesion of the right MCA with involvement of the structures of the right cerebral hemisphere (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1
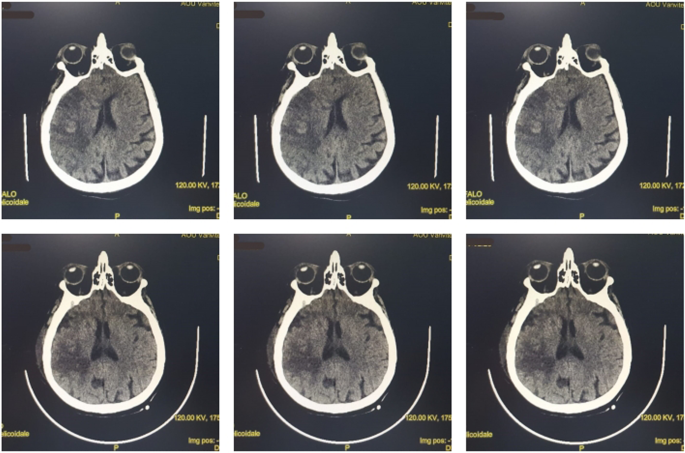
Brain computed tomography (CT). Top row: CT images upon arrival at the intensive care unit. Bottom row: CT images after 10 days of clinical evolution
Full size image
The results of blood, urine, and infection investigations, including bronchial aspirate, were negative, as was the procalcitonin test. Chest x-ray and lung CT did not show signs of infection (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2
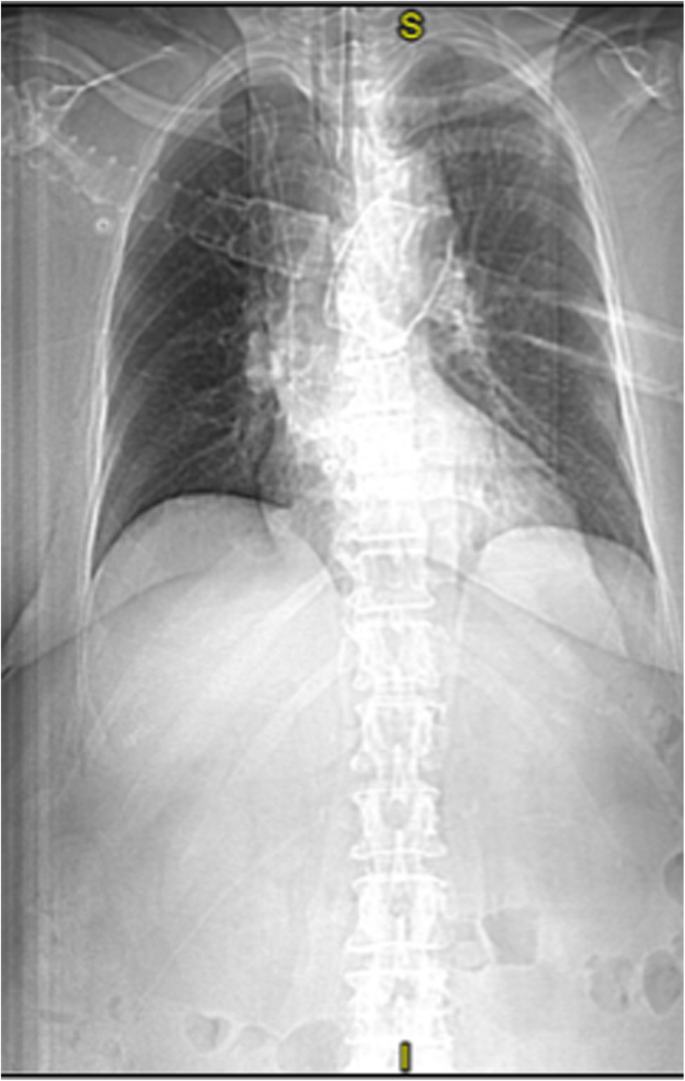
Lung computed tomography
Full size image
The antimicrobial therapy was stopped. Despite the administration of acetaminophen and external cooling, there was no reduction in body temperature (maximum body temperature [TCmax], 40.5 °C) during first 4 days after ICU admission. After thoroughly ruling out infections and the other noninfectious etiologies, the diagnosis of central fever was made. After informing family members and having received written informed consent, a continuous infusion of diclofenac sodium (DFC) was decided. After an initial bolus of DCF (0.2 mg/kg in 100 ml of saline solution in 30 minutes), a continuous infusion (75 mg in 50 ml of saline solution) was started. The dosage of DCF (0.004–0.08 mg/kg/hour) was managed on the basis of the response of body temperature. The DCF infusion was discontinued if the patient’s body temperature was less than 37.5 °C for more than 12 hours with a dose of 0.004 mg/kg/hour.
During the infusion, the patient’s complete blood count, blood pressure, and liver and kidney function were strictly monitored. Continuous monitoring of temperature using an esophageal probe was adopted.
A reduction in body temperature was recorded from the first day of treatment (TCmax, 38.5 °C), and after 5 days of treatment, the patient’s body temperature was constantly below 37.5 °C, and the DCF infusion was stopped (see Table 1).
Table 1 Temperature, heart rate, arterial pressure, and oxygen saturation trends
Full size table
During treatment with DCF, complete blood count, blood pressure, and urinary output were within the normal range. Transient increases in glutamic oxaloacetic transaminaseglutamic (GOT) or aspartate aminotransferase (AST), serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase (GPT) or alanine transaminase (ALT), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) were recorded, with immediate normalization after the suspension. Renal function was preserved (creatinine, 0.83 mg/dl; glomerular filtration rate, 72 ml/minute/1.73m2).
The patient showed clinical improvement with increased neurological status (GCS score, 9) and hemodynamic stability. Neurological examination revealed evidence of left hemiparesis. During hospitalization, the patient’s neurological status showed no improvement. She died of infectious complications 40 days after admission. The patient’s family members were informed prior to the publication of this article, and they provided written informed consent regarding both the case and the images used.
Discussion
The main international guidelines (see Table 2) regarding stroke management pay attention to temperature monitoring and management, but no recommendation is made regarding antipyretic treatment [4,5,6,7]. In the critical care management of patients with stroke, temperature control appears to have great value [8, 9]. An appreciable reduction in temperature can be achieved by physical cooling, but it can cause chills and vasoconstriction [2]. Surface and endovascular cooling devices can be used. Because fever is caused by a prostaglandin elevation altering thermoregulation control in the hypothalamus, an appropriate intervention is to block this process. Typical antipyretics, including acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, are believed to interfere with prostaglandin synthesis. However, reports have suggested that neurogenic fevers are somewhat resistant to traditional pharmacologic therapies; indeed, the use of oral antipyretics to lower body temperature appears inadequate [2]. Acetaminophen in the doses recommended for the treatment of fever has limited efficacy in critically ill patients and often exceeds the maximum daily dose with high risk of liver toxicity [1].
Table 2 Temperature management in international guidelines
Full size table
In the literature, eight studies have investigated the use of DCF for fever control in ICU patients with acute brain damage [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17] (see Table 3). For the treatment of our patient, we relied on the experience of Cormio and Citerio [15]. As already demonstrated, continuous infusion of DCF, even at low doses, provides more stable control of body temperature, minimizing possible adverse reactions. Continuous infusion of DCF was evaluated in two other studies, with similar results [13, 16].
Table 3 Characteristics of studies examining antipyretic effects of diclofenac in the intensive care unit
Full size table
Two reports investigated single-shot intravenous use of DCF. In one of the first studies on the subject, DCF 0.2 mg/kg was administered, providing an effective antipyretic effect and avoiding major adverse reactions [11]. In a more recent study, a dose of DCF 75 mg was administered [16]. The authors recorded a reduction in body temperature, but adverse effects were reduced cerebral perfusion pressure and brain hypoxia, both associated with a worse patient outcome.
Other routes of administration have also been evaluated [10, 14, 16]. Low-dose intramuscular DCF is effective for fever control, but it can cause hypotensive episodes that require vasopressor treatment [15].
In our single experience, continuous infusion of DCF allowed normalization of body temperature in the absence of major adverse reactions.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the development of fever in patients with brain injury admitted to the ICU is a cause of worse clinical outcome. It is essential to diagnose and treat fever in patients with stroke as rapidly as possible. We observed that a low-dose DCF infusion was effective in treating fever, without systemic side effects. This treatment may be suggested as an alternative to conventional antipyretic drugs, but additional clinical trials are required.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
1.
Wrotek SE, Kozak WE, Hess DC, Fagan SC. Treatment of fever after stroke: conflicting evidence. Pharmacotherapy. 2011;31(11):1085–91.
Article
Google Scholar
2.
Meier K, Lee K. Neurogenic fever: review of pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. J Intensive Care Med. 2017;32(2):124–9.
Article
Google Scholar
3.
Gowda R, Jaffa M, Badjatia N. Thermoregulation in brain injury. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;157:789–97.
Article
Google Scholar
4.
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. 2018 Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018;49:e46–e110.
Article
Google Scholar
5.
Boulanger J, Lindsay M, Gubitz G, et al. Canadian Stroke Best Practice Recommendations for Acute Stroke Management: Prehospital, Emergency Department, and Acute Inpatient Stroke Care, 6th Edition, Update 2018. Int J Stroke. 2018;13(9):949–84.
CAS
Article
Google Scholar
6.
Ntaios G, Dziedzic T, Michel P, et al. European Stroke Organisation (ESO) guidelines for the management of temperature in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2015;10(6):941–9.
Article
Google Scholar
7.
Intercollegiate Stroke Working Party. National clinical guideline for stroke. 5th ed. London: Royal College of Physicians; 2016. https://www.bgs.org.uk/sites/default/files/content/resources/files/2018-06-05/national_guidelines_2016.pdf
8.
McDermott M, Jacobs T, Morgenstern L. Critical care in acute ischemic stroke. Handb Clin Neurol. 2017;140:153–76.
CAS
Article
Google Scholar
9.
Bevers MB, Kimberly WT. Critical care management of acute ischemic stroke. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2017;19(6):41.
Article
Google Scholar
10.
Zandstra DF, Stoutenbeek CP, Alexander JP. Antipyretic therapy with diclofenac sodium: observations on effect and serious side effects in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 1983;9(1):21–3.
CAS
Article
Google Scholar
11.
Pesenti A, Riboni A, Basilico E, Grossi E. Antipyretic therapy in ICU patients: evaluation of low dose diclofenac sodium. Intensive Care Med. 1986;12(5):370–3.
CAS
Article
Google Scholar
12.
Cormio M, Citerio G, Spear S, Fumagalli R, Pesenti A. Control of fever by continuous, low-dose diclofenac sodium infusion in acute cerebral damage patients. Intensive Care Med. 2000;26(5):552–7.
CAS
Article
Google Scholar
13.
Caricato A, Conti G, Mercurio G, Mancino A, Santilli F, Antonelli M, Proietti R. Continuous low-dose diclofenac infusion for fever control in patients with acute neurological lesions. Can J Anaesth. 2004;51(9):950–1.
Article
Google Scholar
14.
Cormio M, Ergoli C, Citerio G, Portella G, Pesenti A. Subcutaneous diclofenac at low dose is very effective in treating fever with an accompanying reduction in intracerebral pressure in NICU patients [abstract]. Crit Care. 2004;8(Suppl 1):P316.
Article
Google Scholar
15.
Cormio M, Citerio G. Continuous low dose diclofenac sodium infusion to control fever in neurosurgical critical care. Neurocrit Care. 2007;6(2):82–9.
CAS
Article
Google Scholar
16.
Schiefecker AJ, Pfausler B, Beer R, et al. Parenteral diclofenac infusion significantly decreases brain-tissue oxygen tension in patients with poor-grade aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Crit Care. 2013;17(3):R88.
Article
Google Scholar
17.
Picetti E, Servadei F, Reverberi C, et al. Low-dose intramuscular diclofenac sodium for fever control in acute brain injury. World Neurosurg. 2016;95:241–5.
Article
Google Scholar
Download references

Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου