Impact of Long‐Wavelength Ultraviolet A1 and Visible Light on Light‐Skinned Individuals
Indermeet Kohli, Raheel Zubair, Alexis B. Lyons, Amanda F. Nahhas, Taylor L. Braunberger, Mohsen Mokhtari, Eduardo Ruvolo, Henry W. Lim, Iltefat H. Hamzavi
Pages: 1285-1287 | First Published: 25 July 2019

Solar radiation is known to be a major contributor to the development of skin cancer. Most sunscreen formulations, including those with broad spectrum, offer minimal protection in long wavelength ultraviolet A1 (UVA1; 370–400 nm) and visible light (VL; 400–700 nm) domain. There is limited information regarding the impact of this broad waveband (VL + UVA1, 370‐700 nm) on those with light skin. This study demonstrates that VL + UVA1 induces clinically perceptible erythema. This is a novel finding since the erythemogenic spectrum of sunlight has primarily been attributed to ultraviolet B and short wavelength ultraviolet A (320–340 nm).
The Course of Immune Stimulation by Photodynamic Therapy: Bridging Fundamentals of Photochemically Induced Immunogenic Cell Death to the Enrichment of T‐Cell Repertoire
Shubhankar Nath, Girgis Obaid, Tayyaba Hasan
Pages: 1288-1305 | First Published: 10 October 2019

Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a potentially immunogenic anti‐tumor treatment modality that utilizes the spatiotemporal combination of a photosensitizer (PS), light, and oftentimes oxygen, to generate therapeutic cytotoxic molecules. Upon light irradiation (PDT), tumor cells undergo cell‐death pathways and release damage‐associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and tumor‐specific antigens (TSAs) in the tumor microenvironment. Dendritic cells (DCs) internalize the TSAs and activate T cells, which undergo clonal expansion. As a result, tumor‐reactive T cell repertoire is thought to be enriched. Activated T cells reach the primary or metastatic tumor sites via systemic circulation and eliminate the tumors.
Photochemical Properties of trans‐[Ru(NH3)4(bpa)(L)]2+ (L = py, isn, 4‐acpy or 4‐pic)
Wagner Batista dos Santos, Kelly Aparecida Encarnação Amorim, Anderson Dourado Galvão, Fabricio Tarso Moraes, Dario Batista Fortaleza, Luiz Alfredo Pavanin
Pages: 1306-1310 | First Published: 23 June 2019

Photosubstitution processes in ruthenium amines of the type trans‐[Ru(NH3)4LL′]+2 where L are nitrogenous heterocyclic ligands, pyridine (py), isonicotinamide (isn), 4‐acetylpyridine (4‐acpy) and 4‐picoline (4‐pic) and the 1,2‐bis(4‐pyridyl)ethane (bpa) ligand, lead to the substitution of nitrogenous ligands by water molecules, however, this change is dependent on the wavelength used. The characteristic of the binder is also another factor to be considered since the process of labilization did not occur for all ligands, isn, and 4‐acpy, which gives these complexes photochemical stability and therefore it is possible to classify them as not reactive.
Photocatalytic Degradation of a Chlorinated Organic Chemical Using Activated Carbon Fiber Coupled with Semiconductor
Ashitha Gopinath, Kadirvelu Krishna
Pages: 1311-1319 | First Published: 06 June 2019

A reusable photocatalyst developed based on activated carbon fibre and semiconductor was successfully utilized for degradation of 2, 4‐dichlorophenol which is priority pollutant listed by US EPA. Degradation efficiency of 94.3% was achieved when ratio of pollutant to Zn load was 1.37:1. Photogenerated holes were identified to be the prime species responsible for degradation. Leaching of Zn2+ into the solution was found to be 0.199 µg mL−1. Further, seed germination studies proved that ZnO could be used for plant growth.
Nano‐WO3‐SO3H as a New Photocatalyst Insight Through Covalently Grafted Brønsted Acid: Highly Efficient Selective Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohols to Aldehydes
Saber Hosseini, Ali Amoozadeh, Yasaman Akbarzadeh
Pages: 1320-1330 | First Published: 16 July 2019

Nano‐WO3‐supported sulfonic acid (nano‐WO3‐SO3H) has been synthesized as a new heterogeneous solid acid photocatalyst. This efficient and robust photocatalyst has been successfully applied for the selective photo‐catalytic oxidation of aromatic alcohols to the corresponding aldehydes in the presence of nitrobenzene as available industrial oxidant under blue LED irradiation.
Solvothermal synthesis of WO3/TiO2/carbon fiber composite photocatalysts for enhanced performance under sunlight illumination
Zeynep Balta, Esra Bilgin Simsek, Dusan Berek
Pages: 1331-1338 | First Published: 10 May 2019

Visible light activated WO3/TiO2/Carbon fiber composite catalysts were prepared by solvothermal technique. Characterization tests showed successful functionalization of the WO3/TiO2 nanoparticles with CFs. The ternary composite catalyst displayed superior photocatalytic activity when compared with WO3/CF and WO3/TiO2 catalysts under both UV‐A and visible light illumination. The remarkable photocatalytic activity of the WO3/TiO2/CF composite catalyst can be dedicated to (1) coupling effect of TiO2 and WO3, reduced bandgap; (2) decreased electron–hole recombination rate due to electron trapping by carbon fiber’s conduction band; and (3) as well as synergetic effect between adsorption and photocatalysis.
Photoacidity of the 7‐Hydroxyflavylium Cation
Amna Aqdas, Farhan Siddique, Reed Nieman, Frank H. Quina, Adelia J. A. Aquino
Pages: 1339-1344 | First Published: 25 June 2019

A theoretical description of the photodissociation of the excited singlet state of the 7‐hydroxyflavylium cation, the fundamental chromophoric moiety of anthocyanin natural plant pigments.
pH and Charge Effects Behind the Interaction of Artepillin C, the Major Component of Green Propolis, With Amphiphilic Aggregates: Optical Absorption and Fluorescence Spectroscopy Studies
Isamara Julia Camuri, Adriano Batista da Costa, Amando Siuiti Ito, Wallance Moreira Pazin
Pages: 1345-1351 | First Published: 21 May 2019

Reference for the preference of Artepillin C to interact with amphiphilic aggregates (representing the model membranes used in this study) in its neutral state. The interaction is even higher in the fluid state of the lipid vesicles.
Geometry Effects on Light‐Harvesting Complex's Light Absorption and Energy Transfer in Purple Bacteria
Lingyu Zeng, Zeyang Liao, Xue‐hua Wang
Pages: 1352-1359 | First Published: 06 June 2019
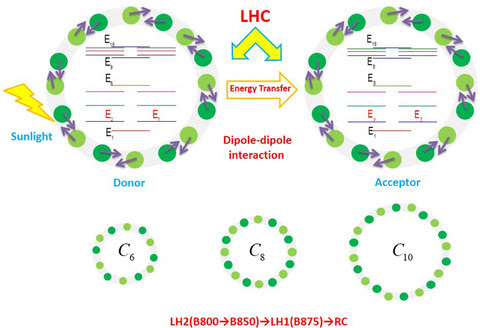
Light‐harvesting complexes (LHC) in photosynthetic organisms perform the major function of light absorption and energy transportation. We construct a geometric model of Rs. Molischianumin in which the geometric parameters such as ring diameter, fold symmetry order and dipole directions can be modified. We study how the absorption spectrum and energy transfer rate of the LHC depend on different geometric parameters. Our results here may find applications in designing highly efficient photovoltaic cell and other artificial photosynthetic systems.
Quantitative Effects of Pigmentation on the Re‐absorption of Chlorophyll a Fluorescence and Energy Partitioning in Leaves
Brian Ospina Calvo, María Gabriela Lagorio
Pages: 1360-1368 | First Published: 13 August 2019

Chlorophyll fluorescence is used to study the adjustment of photosystem stoichiometry, the distribution of the absorbed energy and the dissipation of heat in leaves with or without anthocyanins.
The Growth‐promoting Mechanism of Unusual Spectroscopic Form of LH2 (LH4) from Rhodopseudomonas palustris CGA009 in Low Light
Xiaolan Zhao, Chungui Zhao, Suping Yang, Jiafu Luo
Pages: 1369-1375 | First Published: 22 June 2019

A pucBAd deletion mutant of Rhodopseudomonas palustris CGA009 was constructed and presents lower growth rate under low light intensity. The deletion of pucBAd of CGA009 contains no LH4 and only LH2 complexes under low light conditions. LH4 has higher energy transfer activity than that of LH2, and it can provide more photons with higher energetic state for photosynthesis.
Enzymatic Conversion of Cypridina Luciferyl Sulfate to Cypridina Luciferin with Coenzyme A as a Sulfate Acceptor in Cypridina (Vargula) hilgendorfii
Mitsuhiro Nakamura, Kazuo Matsuda, Misaki Nakamura, Kyohei Yamashita, Tomoko Suzuki, Satoshi Inouye
Pages: 1376-1386 | First Published: 23 June 2019

Cypridina luciferyl sulfate is converted to Cypridina luciferin by Cypridina (Vargula) sulfotransferase with 3'‐phosphoadenosine‐5'‐
Melatonin Receptor Mel1b‐ and Mel1c‐mediated Green Light Induced the Secretion of Growth Hormone in Anterior Pituitary of Chicks
Liang Yue, Xiaojing Qin, Xinfeng Liu, Zixu Wang, Yulan Dong, Yaoxing Chen, Jing Cao
Pages: 1387-1394 | First Published: 21 May 2019

Monochromatic green light promotes the secretion of plasma melatonin. Melatonin influences the expression of Pit‐1 and the secretion of growth hormone in the adenohypophysis cells through melatonin receptor Mel1b and Mel1c.
Relation of Photochemical Internalization to Heat, pH and Ca2+ Ions
Tet Htut Soe, Tomotaka Nanjo, Kazunori Watanabe, Takashi Ohtsuki
Pages: 1395-1402 | First Published: 29 July 2019

Photochemical internalization (PCI) is a strategy to utilize light and photosensitizers for the endosomal membrane destabilization to release endocytosed macromolecules entrapped in endosomes. We studied the contributions of several factors, including heat, pH and calcium ions, on the PCI mechanism.
Synthesis and In Vitro Biological Evaluation of Psoralen‐Linked Fullerenes
Akiko Hashimoto, Takeji Takamura‐Enya, Yoshimitsu Oda
Pages: 1403-1411 | First Published: 26 June 2019
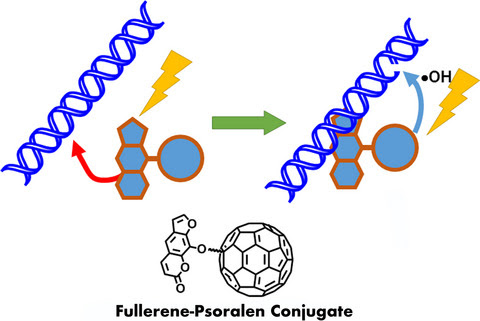
Psoralen‐conjugated fullerenes were synthesized. Psoralen is a well‐known DNA‐binding molecule via the cross‐linking pathway with pyrimidine moiety under UVA conditions. Fullerene can damage DNA by ROS formation under UVA conditions. Combination of these properties of psoralen and fullerene were checked by DNA scission activity, ROS formation ability and genotoxicity using the bacterial detection system. One of synthesized compounds was also found to be cytotoxic to several cancer cell lines.
Antiphotoaging and Antimelanogenesis Properties of Ginsenoside C‐Y, a Ginsenoside Rb2 Metabolite from American Ginseng PDD‐ginsenoside
Xiao‐yi Liu, Yong‐Kun Xiao, Eunson Hwang, Jeong Jee Haeng, Tae‐Hoo Yi
Pages: 1412-1423 | First Published: 10 May 2019
A Peptide YGDEY from Tilapia Gelatin Hydrolysates Inhibits UVB‐mediated Skin Photoaging by Regulating MMP‐1 and MMP‐9 Expression in HaCaT Cells
Zhenbang Xiao, Peng Liang, Jiali Chen, Mei‐Fang Chen, Fang Gong, Chengyong Li, Chunxia Zhou, Pengzhi Hong, Ping Yang, Zhong‐Ji Qian
Pages: 1424-1432 | First Published: 23 June 2019

A processed anti‐aging mechanism of YGDEY in the UVB‐induced photoaging HaCaT cells. Green arrows, activation by YGDEY; red bars, inhibition by YGDEY, black arrows, activation; black bar, inhibition.
Significant Associations Between Sun Exposure and Adiposity Were Not Observed in Breast and Prostate Cancer Patients in a Cross‐sectional Analysis
Gary D. Zhang, Lucinda J. Black, Matthew N. Cooper, Robyn M. Lucas, Shelley Gorman
Pages: 1433-1440 | First Published: 29 July 2019
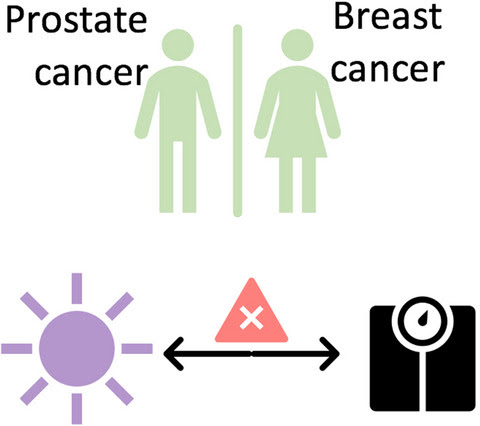
We examined the cross‐sectional relationship between sun exposure and adiposity in a convenience cohort of female breast and male prostate cancer patients. Participants were enrolled in a 3‐month exercise program. Self‐reported questionnaires were used to measure time spent outdoors (previous week, winter, and summer), sex, age, treatment received and physical activity levels. Adiposity measures included body mass index, waist‐hip ratio, and body fat percentage (via DXA). There were no statistically significant associations between time spent outdoors and adiposity after adjusting for sex, age, treatments received, and physical activity.
Optical Spectroscopy as a Method for Skin Cancer Risk Assessment
Eladio Rodriguez‐Diaz, Danielle Manolakos, Holly Christman, Michael A. Bonning, John K. Geisse, Ousama M. A'Amar, David J. Leffell, Irving J. Bigio
Pages: 1441-1445 | First Published: 09 July 2019

This study reports the application of elastic scattering spectroscopy coupled with machine learning to assist in the discrimination of skin lesions that are concerning for malignancy. The method requires no special skin preparation, is non‐invasive, requires minimal training, and allows rapid lesion classification. The classification algorithm was developed on a 950‐lesion training dataset, and diagnostic performance was evaluated against a 357‐lesion testing dataset. The observed sensitivity was 100% (14/14) for melanoma and 94% (105/112) for nonmelanoma skin cancer. The overall specificity was 36% (84/231). ESS has potential to assist physicians in evaluating common benign and malignant skin lesions.


Δεν υπάρχουν σχόλια:
Δημοσίευση σχολίου